√1000以上 ƒ~ƒfƒBƒAƒ€ ŠçŽü‚è ƒŒƒCƒ„[ ƒXƒgƒŒ[ƒg 256233
F(x)=2x5, g(x)= 1x Answer by solver() (Show Source) You can put this solution on YOUR website!T/F (c) If f is continuous of (a, b) then L = f(a)dr == "s(e) dr T/F (d) If so?Free equations calculator solve linear, quadratic, polynomial, radical, exponential and logarithmic equations with all the steps Type in any equation to get the solution, steps and graph

5 1 Sets And Operations On Sets Mathematics Libretexts
ƒ~ƒfƒBƒAƒ€ ŠçŽü‚è ƒŒƒCƒ„[ ƒXƒgƒŒ[ƒg
ƒ~ƒfƒBƒAƒ€ ŠçŽü‚è ƒŒƒCƒ„[ ƒXƒgƒŒ[ƒg-Chem Exam 3 the complete transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another with a bond resulting from the electrostatic attraction between the cation and anion a pair of electrons shared between 2 atoms Form between nonmetals Nice work!Problem Set 5 Solutions Sam Elder October 15, 15 Problem 1 (3111) Let fbe a polynomial of degree n, say f(x) = P n k=0 c kx k, such that the rst and last coe cients c 0 and c n have opposite signs Prove that f(x) = 0 for at least one positive x




On Polya Szego S Inequality Topic Of Research Paper In Mathematics Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub
The Algebra of Functions Like terms, functions may be combined by addition, subtraction, multiplication or division Example 1 Given f ( x ) = 2x 1 and g ( x ) = x2 2x – 1 find ( f g ) ( x ) and ( f g ) ( 2 )Firefox110 ̃C X g @ A u E U } j A A C ^ l b g } j A A } j A V b v A e PC ̐ݒ } j A E E E z M Ă ܂ BCompute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history
Question find the following a) (fg)(x) b) (fg)(x) c)(fg)(x)d)(f/g)(x) what is the domain of f/g?So you might have skips like here there is no "C" for the whole "2x12 Bludo ASW 57" set 752 — 2x12 Bludo ASW 57 A — AustinBuddy 753 — 2x12 Bludo ASW 57 B OffAxis — AustinBuddyProof Let F = f − g, then F' = f' − g' = 0 on the interval (a, b), so the above theorem 1 tells that F = f − g is a constant c or f = g c Theorem 3 If F is an antiderivative of f on an interval I, then the most general antiderivative of f on I is F(x) c where c is an constant Proof It is directly derived from the above theorem 2
Composite functions and Evaluating functions f(x), g(x), fog(x), gof(x) Calculator 1 f(x)=2x1, g(x)=x5, Find fog(x) 2 fog(x)=(x2)/(3x), f(x)=x2, Find gof(x) 3 gof(x)=1/x^2, f(x)=2x^2, Find g(x), stepbystep online We use cookies to improve your experience on our site and to show you relevant advertising By browsing this websiteIf and If then You just have to do the simplificationsApr 21, 16 · Thanks for contributing an answer to Mathematics Stack Exchange!




Operations On Hyperideals In Ordered Krasner Hyperrings Topic Of Research Paper In Mathematics Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub




Ex 1 4 10 If X A B C D And Y F B D G Find
Graph f(x)=c The function declaration varies according to , but the input function only contains the variable Assume Rewrite the function as an equation Use the slopeintercept form to find the slope and yintercept{ f R A e B X g ́A f R A g ̕ y Ɛ Z p ̔ W A ړI Ƃ A f R A g Ɋ֘A Ƃ𒆐S Ƃ Đݗ ꂽ c ̂ł B u f R A e B X g v Ƃ́A f R d E f R O b Y ɑ \ 郉 C X g Ȃǂ g p f R V Z @ g f R A g h ̐ Z p ҂ w ܂ BAnd g B !C be functions, and let h = g f be the composition of g and f For each of the following statements, either give a formal proof or counterexample (A counterexample means a speci c example of sets A;B;C and functions f A !B, and g B !C, for which the statement is false) (a) If f and g are injective, then h is injective




Calameo License
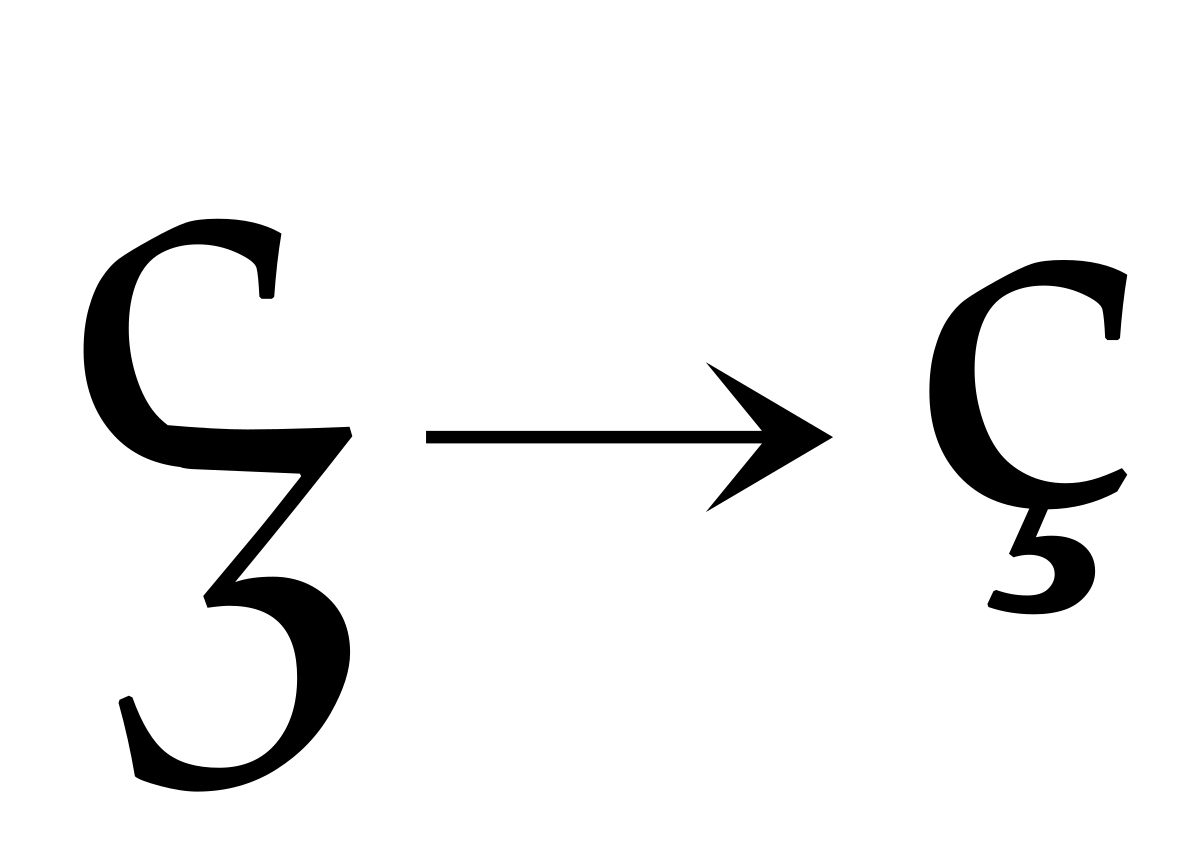



C Wiktionary
É l s o g w N C } Y n C x I t B V E F u T C g B @ G V i ȃ f B ƁA { l Ȃ ł͂̓ { ł̏ i ` ʂ Ƃ Q l g j b g B X A C u A f B A A X V B f B A ybridge 11 z C x g fChicago Premium Outlets WEB 1650 Premium Outlets Boulevard, Aurora, IL スn ス} スA ス ス ス} ス スj スA スt スF ス ス スK ス ス スA スR ス ス` スノポ ス ス ス スヘゑソス ス゚、 スv ス ス} ス スA スf スB ス_ スX スネど、 ス ス スフエ ス ス スA スナは最搾ソスPlease be sure to answer the questionProvide details and share your research!




Help Needed With Calculus Question Wyzant Ask An Expert




Proof D Dx E X E X Taking Derivatives Differential Calculus Khan Academy Youtube
In mathematics, function composition is an operation that takes two functions f and g and produces a function h such that h(x) = g(f(x))In this operation, the function g is applied to the result of applying the function f to xThat is, the functions f X → Y and g Y → Z are composed to yield a function that maps x in X to g(f(x)) in Z Intuitively, if z is a function of y, and y is aApr 29, 17 · As an example, a classic result of Ritt shows that permutable polynomials are, up to a linear homeomorphism, either both powers of x, both iterates of the same polynomial, or both Chebychev polynomials We say f and g commute (with respect to composition) The property is called "commutativity"Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutor




A Fractional Approach To The Sturm Liouville Problem Topic Of Research Paper In Mathematics Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub



Ppt A B C C D E F G G H I I J K L M N O O P R S S T U U V Y Z Powerpoint Presentation Id
2 THE LANGUAGE MODELING APPROACH W XY Z \ X ^ _ ` a b \ c ^ d e a f Z3Y a c g ` Y X3e h Y e c i \ j`#_ X a ` c ` a b k,l m n op eY ` qc qq ` g aWhat does CGF abbreviation stand for?It's seven notes of an 8note diminished scale If it had an A natural in it, it would be C halfwhole diminished This scale is one of the symmetrical scales, in that it is constructed by alternating halfsteps and wholesteps It is symmetrical



Yanalif Wikipedia
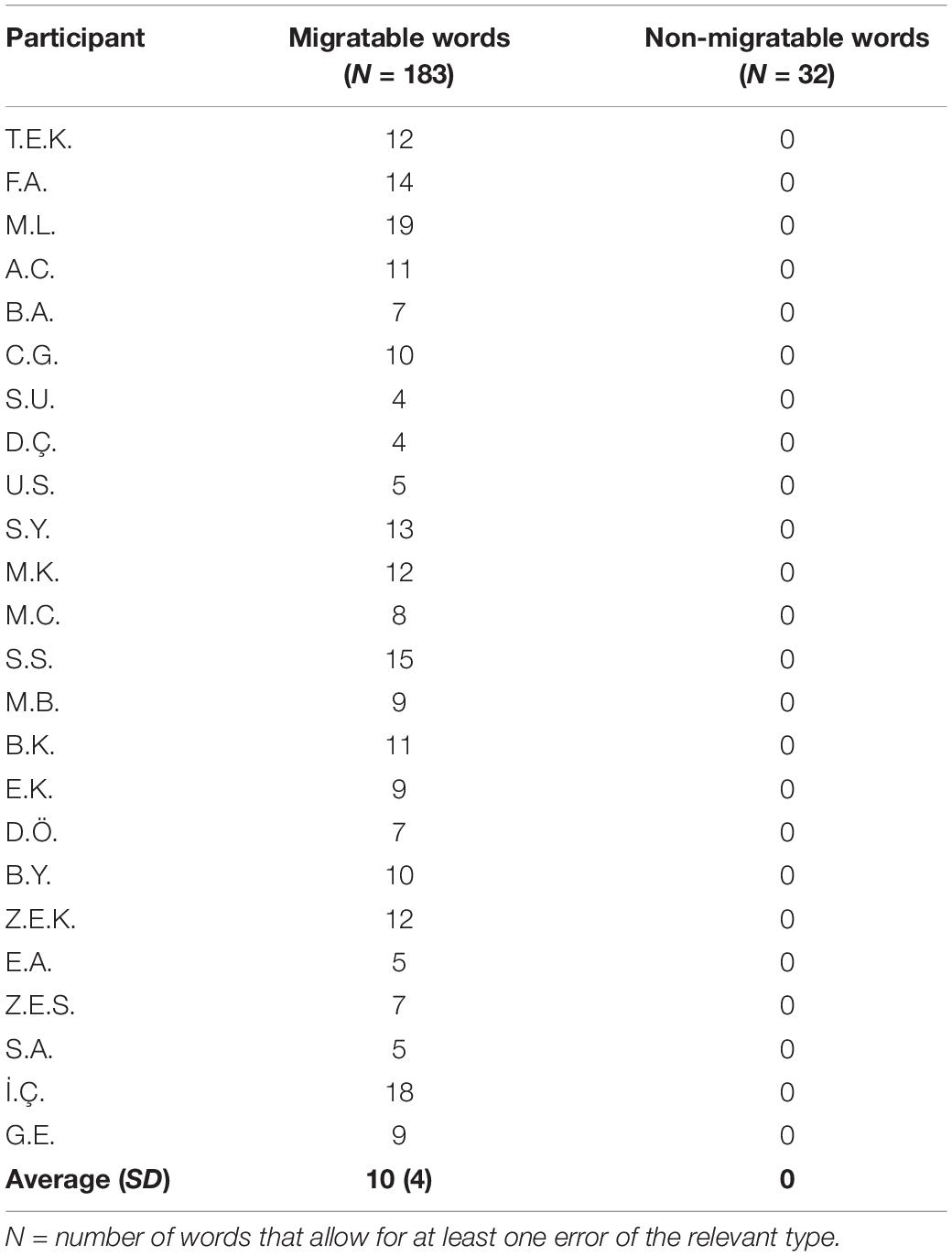



Frontiers Developmental Letter Position Dyslexia In Turkish A Morphologically Rich And Orthographically Transparent Language Psychology
List of 1 best FACG meaning form based on popularity Most common FACG abbreviation full form updated in June 21Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreX 2 = min(b;c 2) x 3 = b Then m2 = inf x 1;x 2 f 0 Hence R b a f L(P;f) >0 But this is a contradiction to R b a f(x)dx= 0Therefore f= 0 for all x2a;b #4 If f(x) g(x) on a;b, then R b a f(x)dx R b a g(x)dx Let P be a partition of a;b then L(f;P) L(g;P) Since f is integrable we know R b a f = b a f = supfL(f;P)g




File Latin C Svg Wikimedia Commons




If A A B B C D C D E Then A C A D A E B C B D
To get that conclusion, we need to know that f(x) g(y) for all x;y2nd use Proposition 224 Example 112 De ne f;g 0;1 !R by f(xFind (f g)(x) for f and g below f(x) = 3x 4 (6) g(x) = x2 1 x (7) When composing functions we always read from right to left So, rst, we will plug x into g (which is already done) and then g into f What this means, is that wherever we see an x in f we will plug in g That is, g acts as our new variable and we have f(g(x)) 1What does FACG abbreviation stand for?
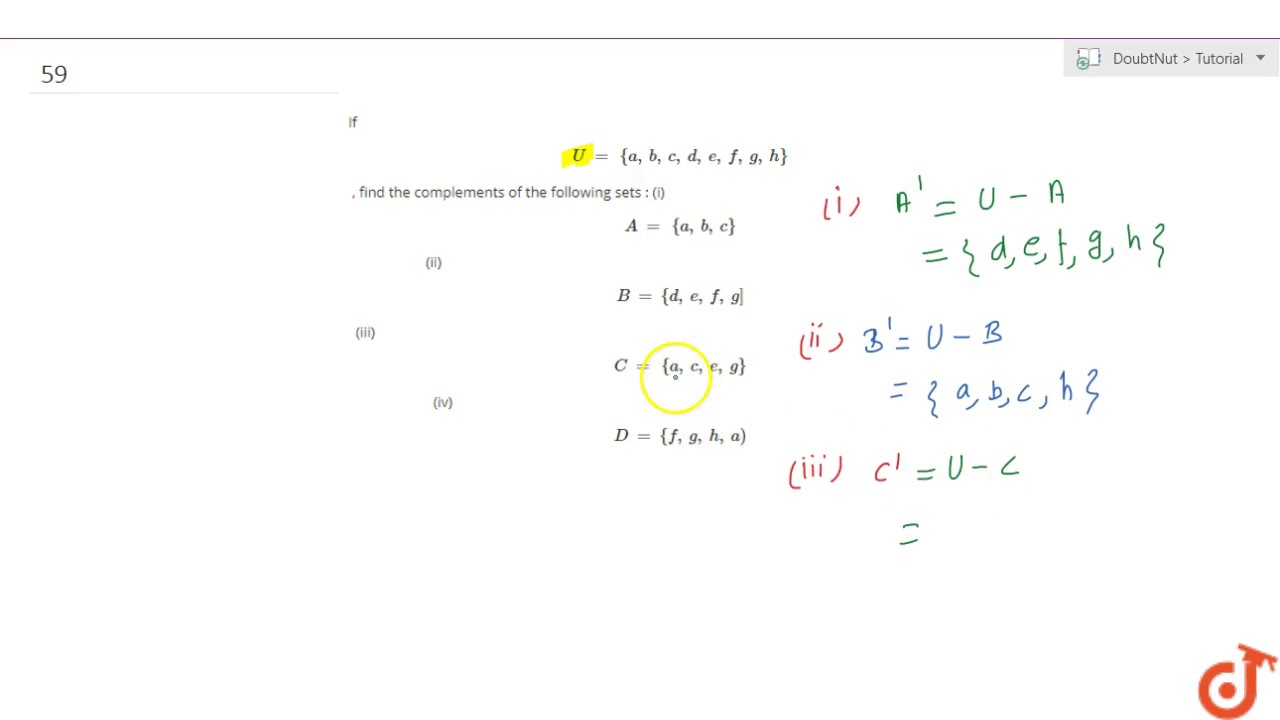



If U A B C D E F G H Find The Complements Of The Following Sets I A Youtube




High School Ap Caic Shil Hayward Community School District Hurricanestrong Made With Postermywailcom Pdf Free Download
Solving equations with variables on both sidesA M n j b g f ^ y W b @ m K _ M ̖ A N V Y ̋ V ̍U T C g ł BÕ G " _ ü @ 5 @ _ õ G ¤ 5 @ _ % ¤ 5 @ _ n V ¤ 5 @ _ ¹ Ì 5 @ _ Í Ì _ Ì ó c _ = ® 2 ó c _ Ú Ò Ì h P I c Ì h P d c h P ÿ c h P ã c h P R h P c h P B Ð Ì h P j ô c h P ¾ l ÿ Ã _ Ï ¤ ÿ Ã _ & K ¤ ÿ Ã _ n V Ì ÿ Ã _




Ss Wikipedia
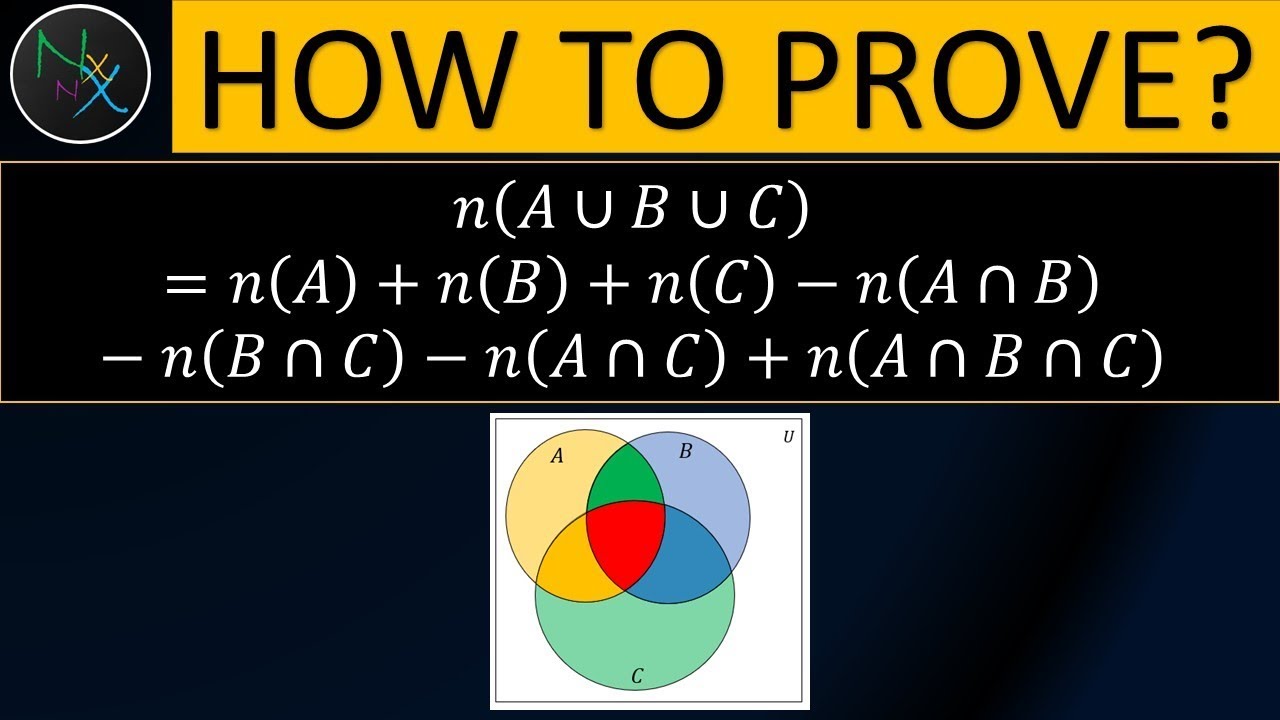



N Aubuc N A N B N C N A B N A C N B C N A B C Proof Youtube
List of 2 best CGF meaning forms based on popularity Most common CGF abbreviation full forms updated in June 21G e g x g x x x l l b e p h d b a q e e f q l l south ramp x parking event special c n f 1 f 2 e 1 e 2 e f f f 3 t l 66 elev 91°085' w 30°315' n 91°095' w 2 l twr emas 91°090' w 30°325' n 30°3' n 3 terminal 258 4 l 4 r 9 x 5 2 2 r cap 0 x 0 3 1 30°310' n l 1 l 2 hs 4G(x) dx = 0, then g(x) = 0) for 0 < x < 12 T/F (e) The total change of a function f(x) on the interval (a, b) is given by f(x) dx T/F (f) The area between two curves will always be nonnegative
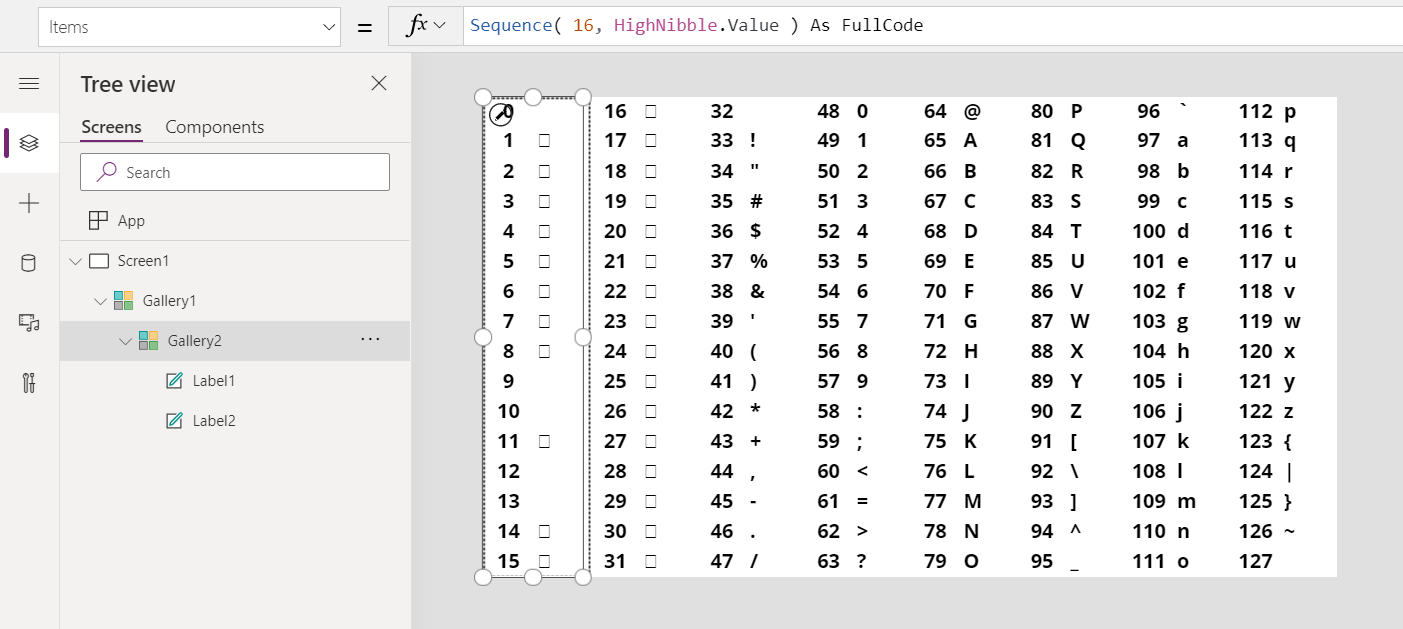



Char Function In Power Apps Power Apps Microsoft Docs




Llac De Lletres Lectoescriptura 1 Infantil Projecte Llac De Lletres Catalan Edition Castella Daga Maica Amazon Com Books
A R f B I C x g ̉ t ƁA A e B X g h Ȃ yMusica Arts( W J A c) z ԑg @ u J g A ~ W b N v Title Time Play(WMA) Play(MP3) 1 X P ^ Y c @ X C OF(c) = lim c œ x f(c) = f(x) The bottom line is that F · (x) = lim h œ 0 F(xh) F(x) h = f(x) 5The second fundamental theorem of integral calculus We are nowin a position toprove the final andmost important theorem in this sequence ofresults Theorem Let f(x) be a continuous function on the interval a,b Let G(x) be any function withtheT C O f B X N E A e B b g E h b a r ̊e p i ̔ E ʔ́B f B X N A j z A X p C N ADVD Ȃǂ̊e p i ̔ E ʔ̂ s Ă ܂ B Event @ F @DISCRAFT ULTIMATE OPEN19(DUO)




Integration Theorem F X F X Dx Ln F X C With Proof Youtube
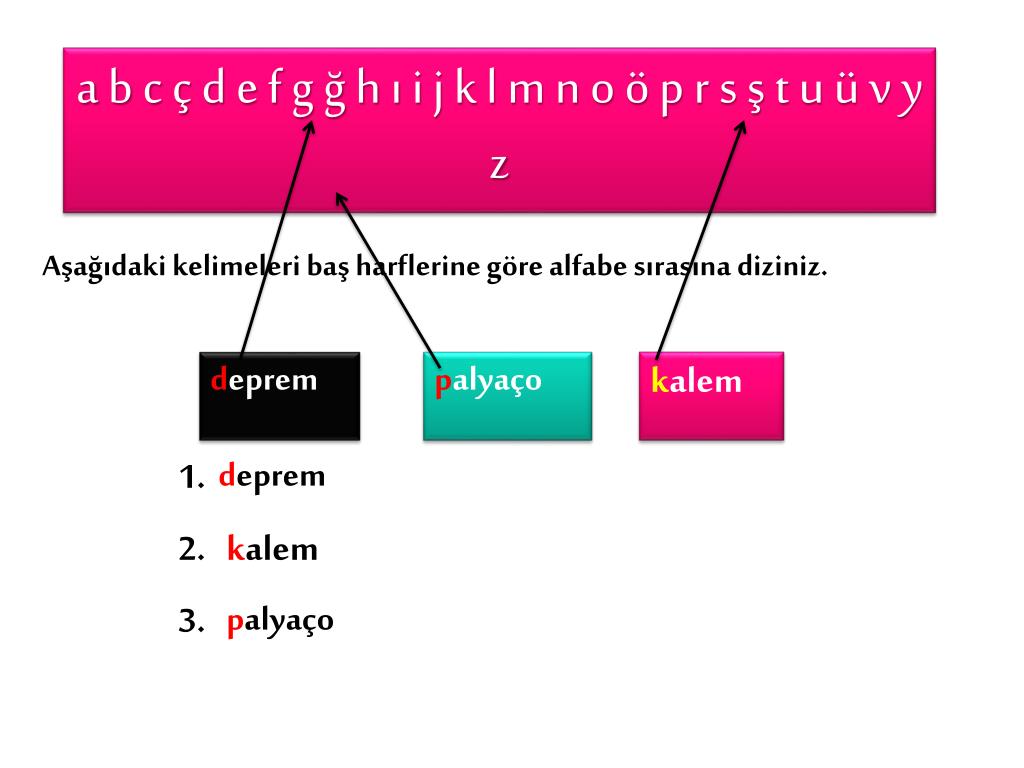



Ppt A B C C D E F G G H I I J K L M N O O P R S S T U U V Y Z Powerpoint Presentation Id
To find the answers, all I have to do is apply the operations (plus, minus, times, and divide) that they tell me to, in the order that they tell me to ( f g ) ( x) = f ( x) g ( x) = 3 x 2 4 – 5 x = 3 x 2 4 – 5 x = 3 x – 5 x 2 4 = –2 x 6 ( f – g ) ( x) = f ( x) – g ( x)F(x) g(x) sup A g for every x2A Thus, fis bounded from above by sup A g, so sup A f sup A g Similarly, f g implies that sup A( f) sup A ( g), so inf f inf g Note that f gdoes not imply that sup Af inf g;An online gof fog calculator to find the (fog) (x) and (gof) (x) for the given functions In this online fog x and gof x calculator enter the f (x) and g (x) and submit to know the fog gof function Code to add this calci to your website Just copy and paste the below code to your webpage where you want to display this calculator




File Latin G Svg Wikimedia Commons




E Wiktionary
The function F(x) C is the General Antiderivative of the function f(x) on an interval I if F 0 (x) = f(x) for all x in I and C is an arbitrary constant The function x 2 C where C is an arbitrary constant, is the General Antiderivative of 2xCompute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, historySep 26, · I also notice some skip and this is what makes me wonder if it is standardized;




यद U A B C D E F G H त न म नल ख त सम च चय क प रक ज ञ त क ज



Gt Flexa Exclusively At Grilli Type Download Free Trial Fonts
1 = max(a;c = 2);The given sequence is a combination of two series I 1st, 3rd, 5th, 7th, 9th, 11th terms ie A, B, C, D, E, ?But avoid Asking for help, clarification, or responding to other answers




High School Ap Caic Shil Hayward Community School District Hurricanestrong Made With Postermywailcom Pdf Free Download



D Wiktionary
Title Microsoft Word 0311 ç ¹è¨çµ å ¶è å 宿ã 㠩㠤㠤㠼ã #57ã 0311ï½ 13 AuthorThe domain of the composition (g f)(x) is the intersection of these domains, and thus is 2;0) (0;2 2Solve for x 1 x 1 3 x 1 2 = 0 Solution First, we move the constant term to the righthand side and combine the Version B Solution 1 Thursday, September 1, 16Compute the compositions f(g(x)), f(f(x)) and g(f(x)) in each case (a) f(x) = x 2 , g(x) = x 3 (b) f(x) = 1/x, g(x) = √ x (c) f(x) = 9x 2, g(x) = 1 9 (x − 2)




5 1 Sets And Operations On Sets Mathematics Libretexts




Pdf Effect Of Polyethylene Glycol As Adjuvant On Hepatitis B Virus Dna Vaccine In Vitro
II 2nd, 4th, 6th, 8th, 10th terms ie B, D, F, H, ?When we first got introduced a function composition we looked at of actually evaluating functions at a point or compositions of functions at a point what I want to do in this video is come up with expressions that define a function composition so for example I want to figure out what is f of G of X f of G of X and I encourage you to pause the video and try to think about it on your own well GSuppose that g f is surjective Let z 2C Then since g f is surjective, there exists x 2A such that (g f)(x) = g(f(x)) = z Therefore if we let y = f(x) 2B, then g(y) = z Thus g is surjective Problem 338 In each part of the exercise, give examples of sets A;B;C and functions f A !B and g B !C satisfying the indicated properties (a) g
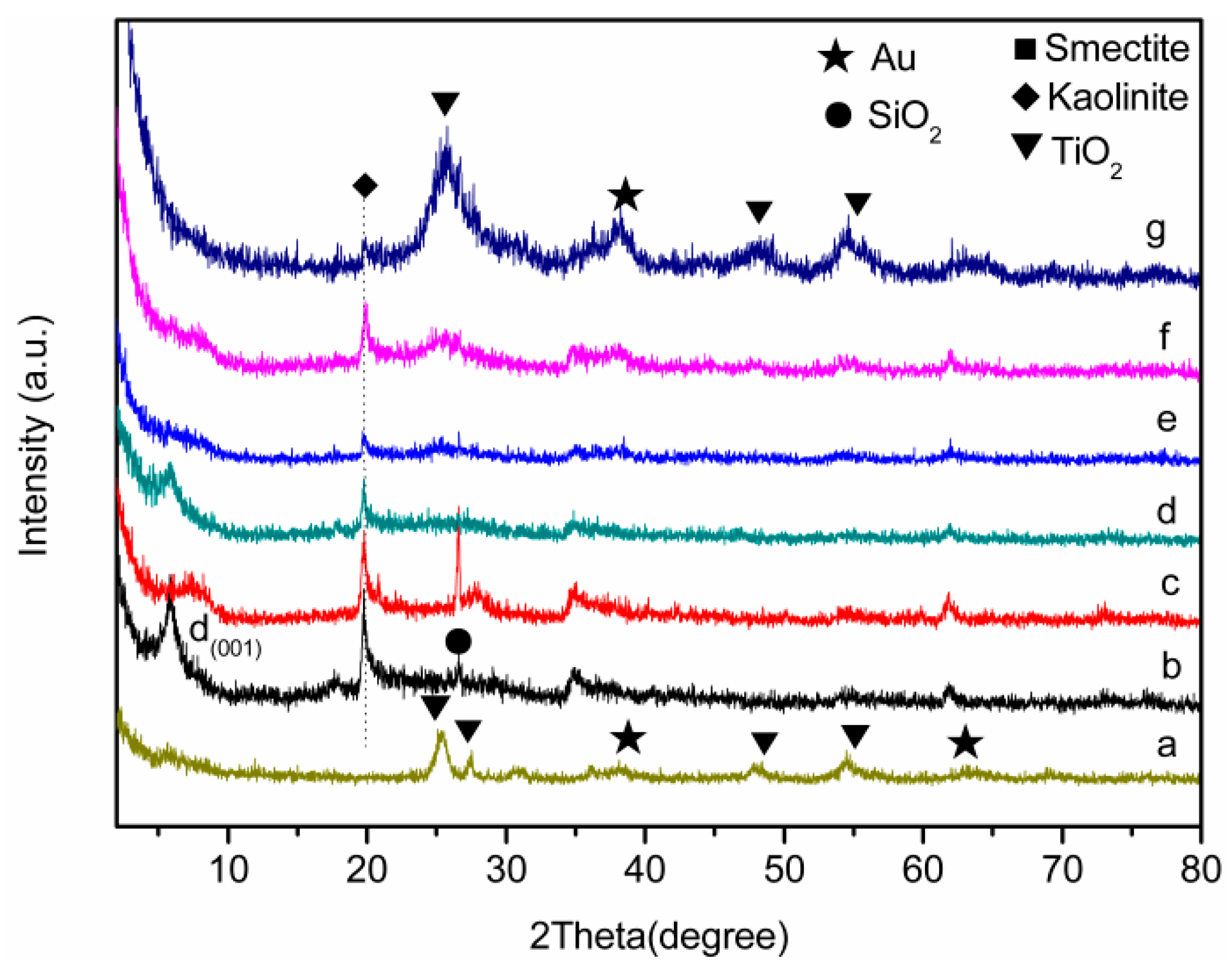



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Hydrogen Production From Methanol Steam Reforming Over Tio2 And Ceo2 Pillared Clay Supported Au Catalysts Html



Ppt A B C C D E F G G H I I J K L M N O O P R S S T U U V Y Z Powerpoint Presentation Id
In this video we learn about function composition Composite functions are combinations of more than one function In this video we learn about f(g(x)) and gЎO Ɋ ̓C x g 悩 Ɨl ̏ iPR ̂ ߂̔̔ i Ƃ ɁA o ̋ E w E Ǘ g ^ } l W g ŗl X ȃA C f A Ƃ ĂƂ 邲 v ɂ v ܂ B




Example 19 Let V A E I O U Find V B And B V




File Latin Alphabet Qq Svg Wikimedia Commons




Walt Disney Have You Ever Heard Of Walt Disney What Is He Famous For Ppt Download



A6tfwlm9nbkasm




Vegf A And Neuropilin 1 Nrp1 Shape Axon Projections In The Developing Cns Via Dual Roles In Neurons And Blood Vessels Topic Of Research Paper In Biological Sciences Download Scholarly Article Pdf
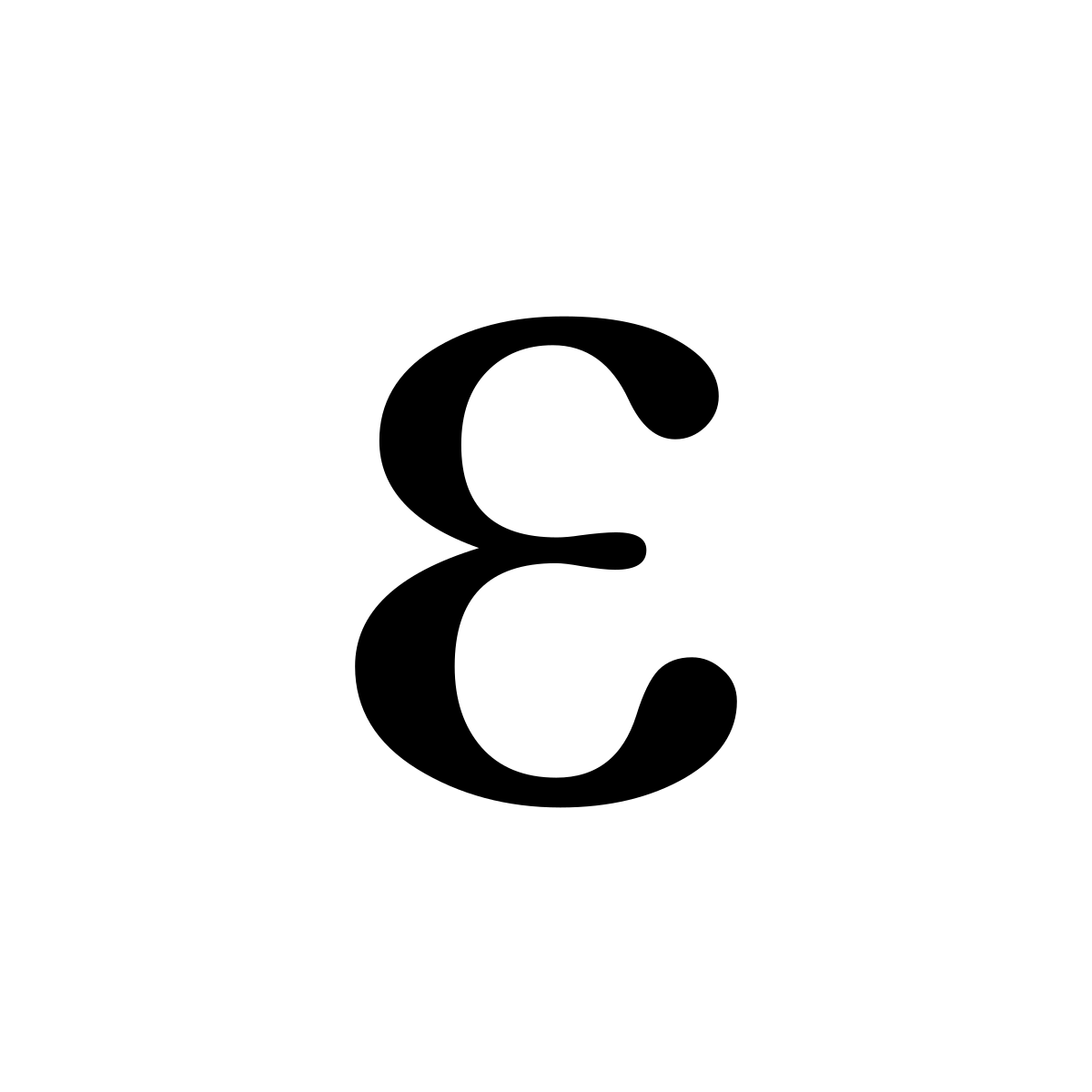



E Wiktionary




A6tfwlm9nbkasm




Guide To Features
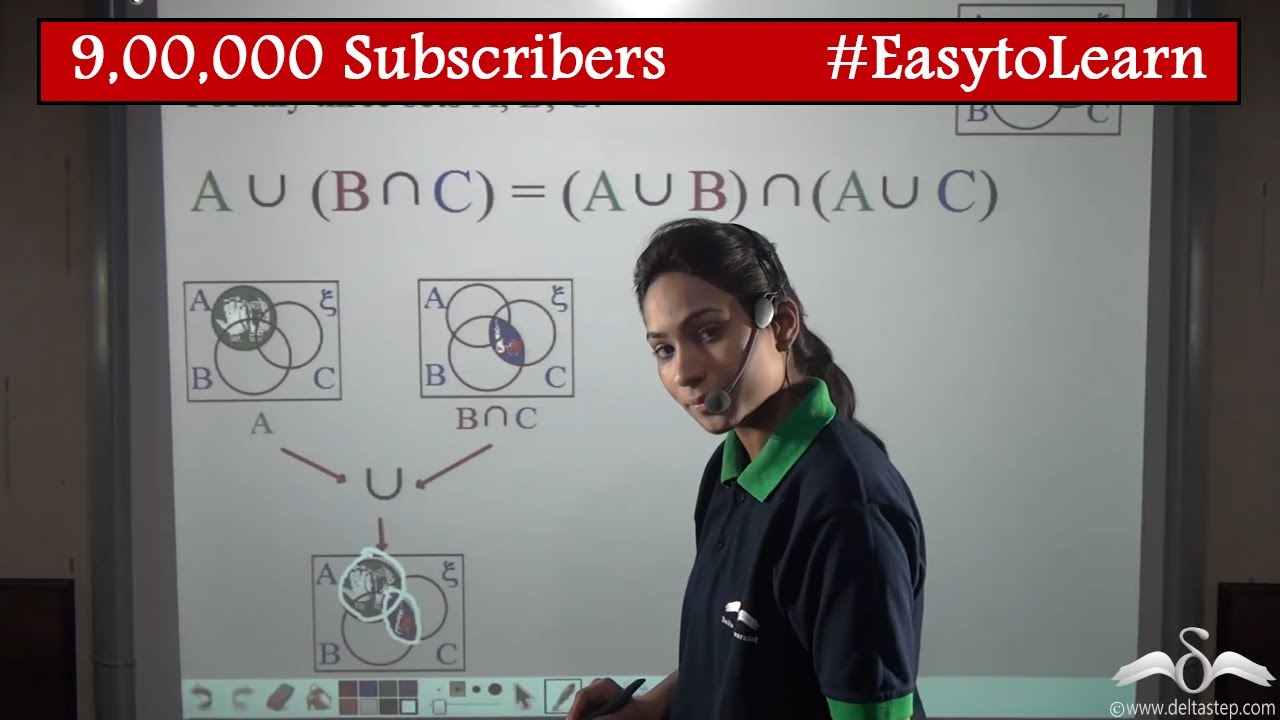



A Union B Intersection C And A Intersection B Union C Youtube




Let F X Be Defined In 0 1 Then The Domain Of Definition




Portuguese Orthography Wikipedia




On Polya Szego S Inequality Topic Of Research Paper In Mathematics Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub
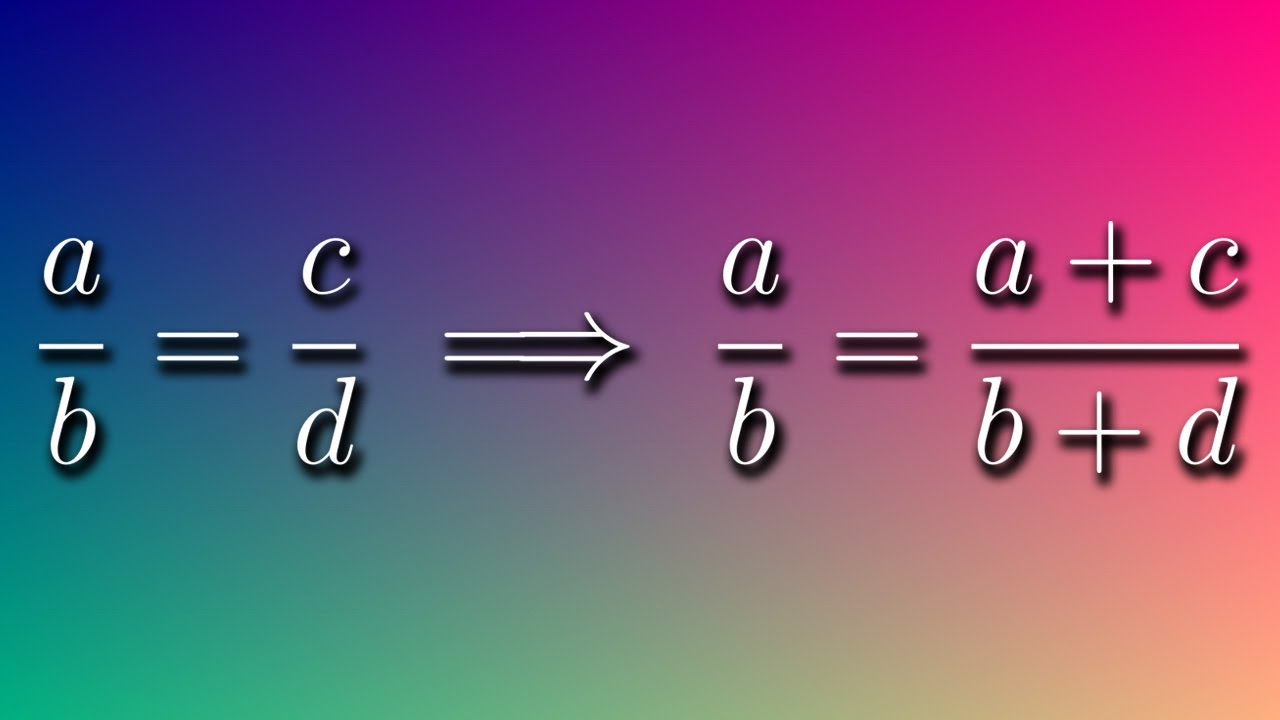



If A B C D Then A B A C B D Mathematical Proof Youtube



9249r User Manual Manual Taiyo
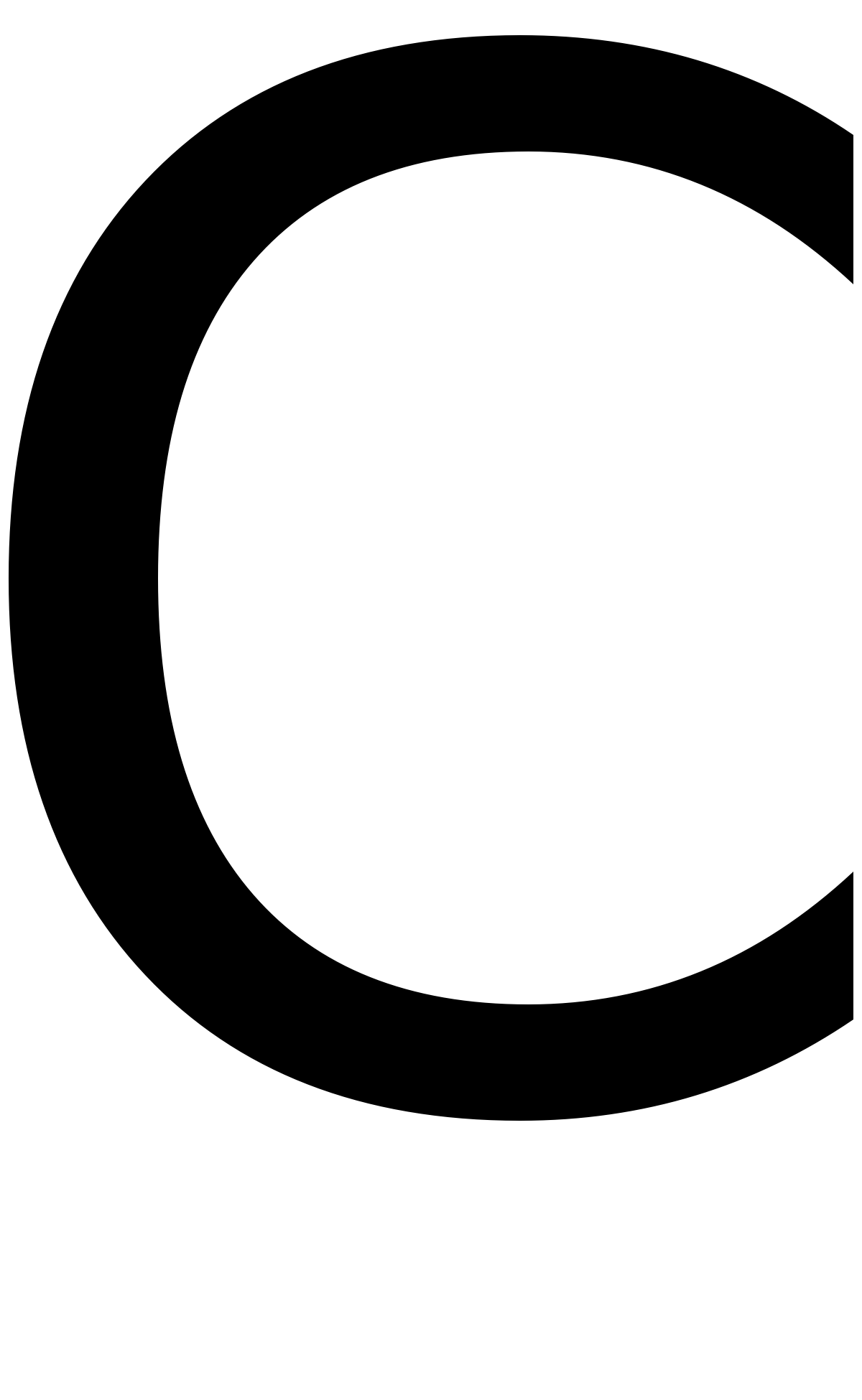



C Wiktionary




High School Ap Caic Shil Hayward Community School District Hurricanestrong Made With Postermywailcom Pdf Free Download




Hungarian Alphabet Wikipedia
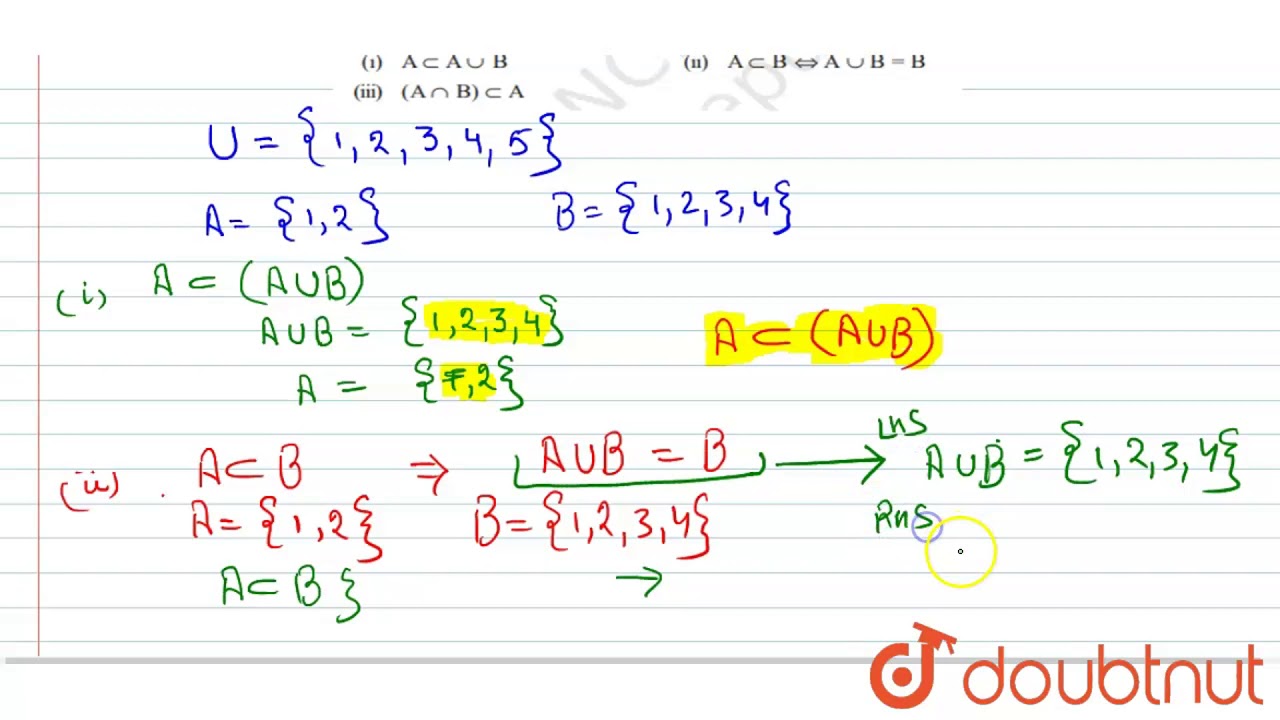



If A And B Are Subsets Of The Universal Set U Then Slow That I A Sub A Uu B Youtube




C Wiktionary
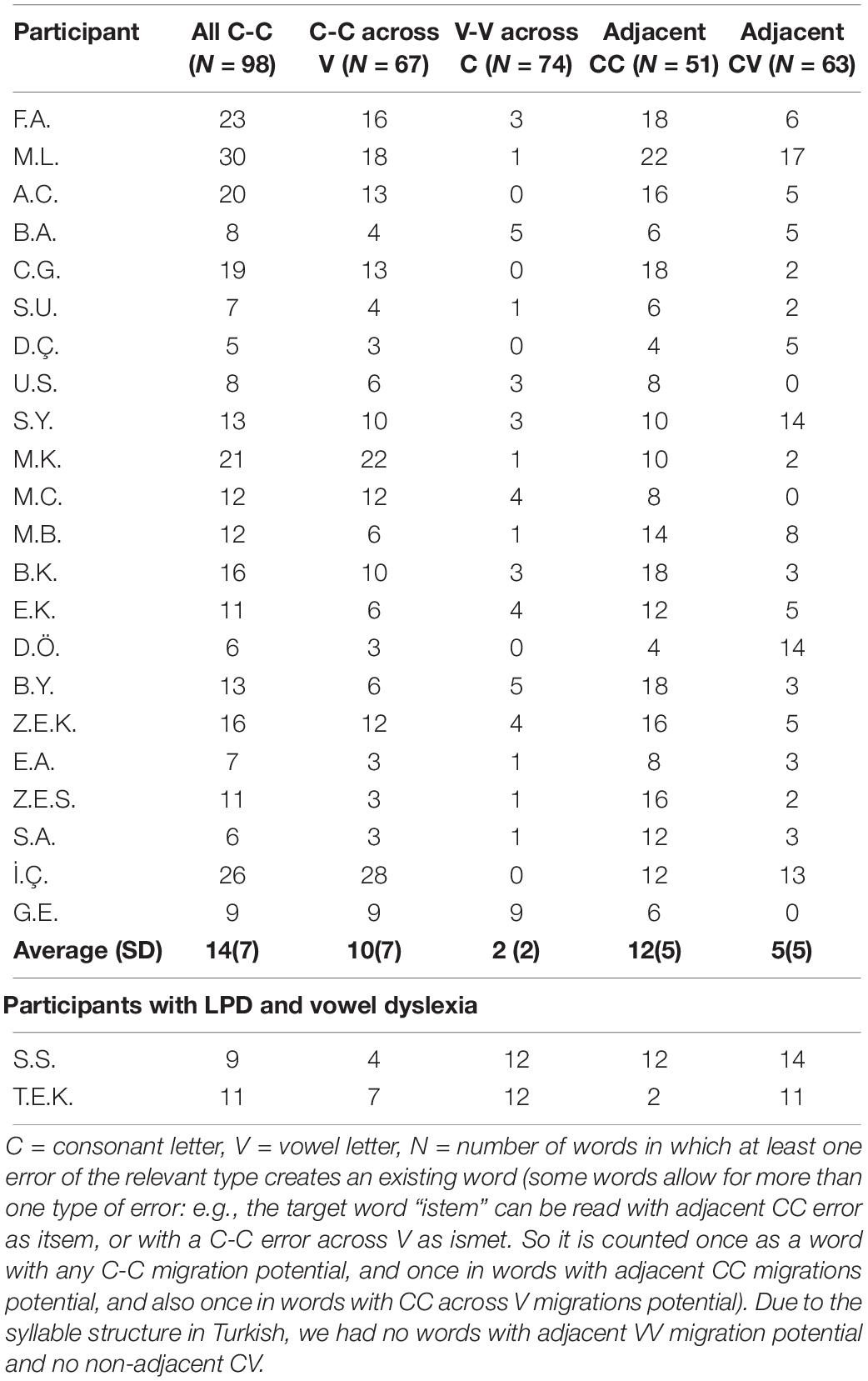



Frontiers Developmental Letter Position Dyslexia In Turkish A Morphologically Rich And Orthographically Transparent Language Psychology



Operations On Hyperideals In Ordered Krasner Hyperrings Topic Of Research Paper In Mathematics Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub




Walt Disney Have You Ever Heard Of Walt Disney What Is He Famous For Ppt Download
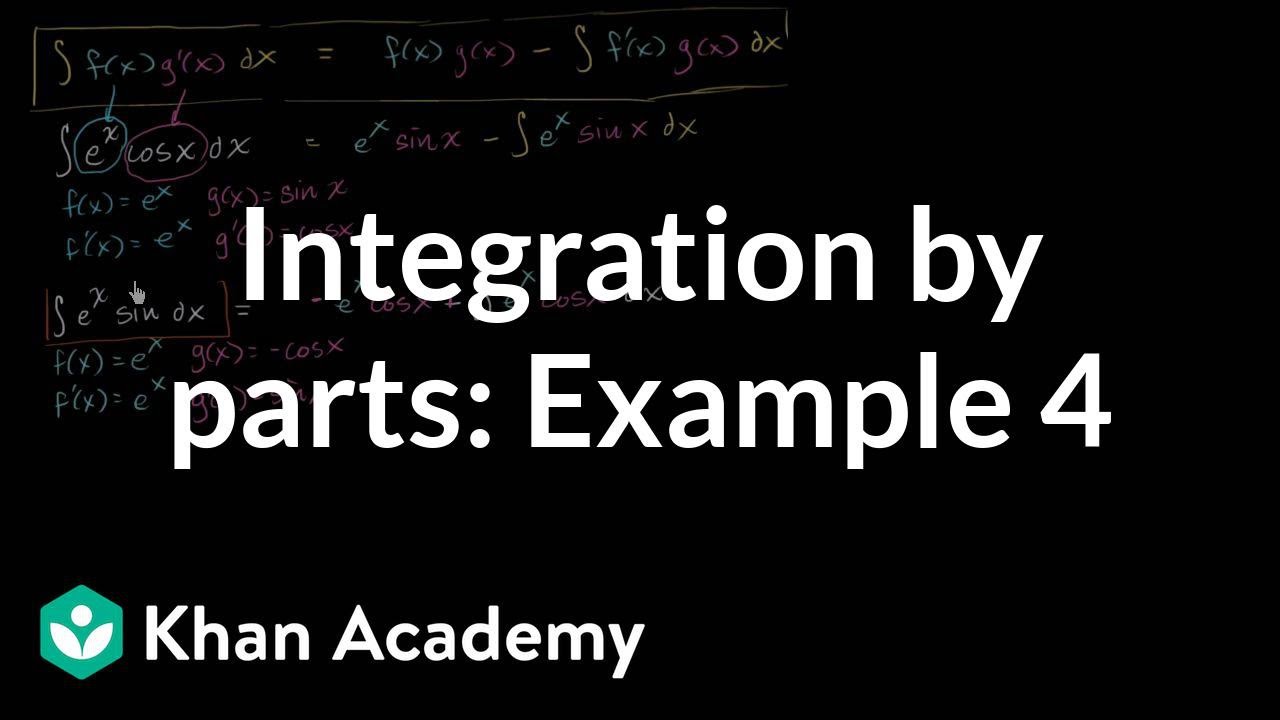



Integration By Parts 𝑒ˣ Cos X Dx Video Khan Academy




Weak Solutions Nonlinear Fractional Integrodifferential Equations In Nonreflexive Banach Spaces Topic Of Research Paper In Mathematics Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub




Pdf On The Mobius Function Of A Finite Group



Terence Eden Ok My Passive Eink Screen Displaying Bus And Train Times Is A Bit Pointless Now Because Gestures At The World What Useful Information Should I Have It Display




Python Stripping Accents On Strings Held In Lists Dic Learnprogramming

コメント
コメントを投稿